Supply control plays a big role in shaping how cryptocurrency tokens behave. One tool that projects use to influence their token economics is a “burn rate,” which is a way of reducing the total number of tokens in circulation over time.
Burning tokens can be a strategy to manage inflation, reward holders, or add scarcity to a coin. In some cases, a consistent burn rate is seen as a sign of long-term sustainability or protocol maturity. Given that it directly impacts available supply, it can influence crypto prices as traders assess how scarcity might affect value.
Understanding what burn rate means and how it works is key for anyone evaluating a project’s tokenomics or exploring the signals behind its price movement.
What Does “Burning” a Token Mean?
In crypto, “burning” a token means permanently removing it from circulation. This is usually done by sending the token to a special wallet address called a “burn address,” which is publicly visible on the blockchain but cannot be accessed by anyone. Once a token is sent there, it’s gone for good.
This process doesn’t delete the token from the blockchain; it simply makes it unusable. That’s why it’s considered a transparent way to reduce supply. Anyone can verify the burn by checking blockchain records, which adds credibility to projects claiming to limit or reduce their token count.
What Is Burn Rate?
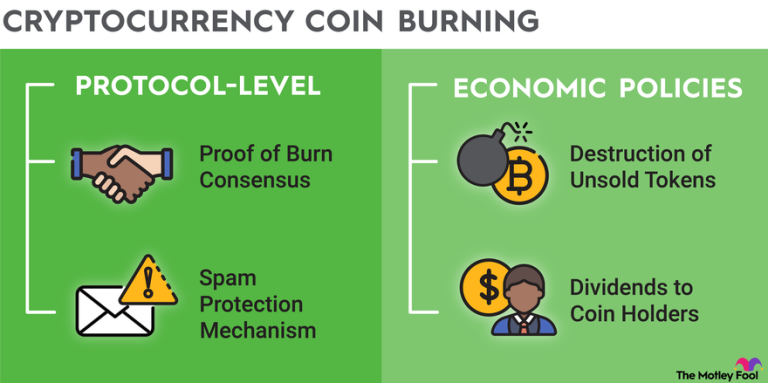
Burn rate refers to how quickly or regularly tokens are removed from circulation, and it’s not just a one-time action. Some projects implement an ongoing or automated burn mechanism that operates based on usage, transaction volume, or fixed schedules.
For example, Binance Coin (BNB) uses a quarterly burn system based on exchange activity, while Ethereum introduced a dynamic fee-burning model with EIP-1559, where part of every transaction fee is burned. These are examples of protocols tying burn rate to actual network use.
Some projects adopt a fixed burn plan, while others let market activity determine the pace. In either case, burn rate is a metric that shows how aggressively a token’s supply is being reduced and how that might shape its long-term economic design.
Why Do Projects Burn Tokens?
One of the most common reasons a project implements token burns is to reduce supply and, in theory, increase scarcity. The logic is simple: if demand remains steady or grows while supply decreases, the token could become more valuable over time.
Some projects burn tokens to offset inflation caused by rewards or token emissions. Others use it as part of a loyalty or rewards model, where tokens collected from transaction fees are destroyed instead of recycled. By limiting the total available supply, burning can also give long-term holders a sense that their network share is becoming more valuable.
It’s also a signaling tool. A transparent, well-planned burn rate can show that a project is serious about managing its token economy, rather than flooding the market with new supply.
Burn Rate vs. Traditional Financial Burn Rate
In traditional finance, “burn rate” refers to how quickly a company spends its cash, especially in early-stage startups. It’s a measure of financial health used to understand how long a company can operate before it needs more funding.
In crypto, the term means something different. It refers to the rate at which tokens are destroyed or removed from circulation, not money being spent. Still, both versions of burn rate deal with sustainability: in startups, it’s about surviving on limited funds; in crypto, it’s about maintaining a healthy token economy.
Risks and Misconceptions Around Burn Rate
While token burning can help manage supply, it does not guarantee rising value. One common misconception is that a high burn rate automatically leads to price increases. In reality, demand still plays a major role. A token with low demand won’t become more valuable because it’s scarcer.
Another risk is when projects promote burn mechanics as a distraction from weak fundamentals or limited real-world use. Aggressive or poorly explained burning strategies can signal desperation rather than a sustainable economic model.
It’s also important to watch for transparency. Projects should clearly outline how their burn mechanisms work, whether burns are manual or automatic, and where the funds come from. Without clear documentation, it’s difficult to assess whether a burn rate is meaningful or simply marketing.
Why Burn Rate Isn’t Just a Buzzword
Burn rate is a key metric in how some crypto projects manage supply and shape their tokens’ long-term behavior. While it shouldn’t be viewed in isolation, understanding how and why tokens are burned can provide helpful insights into a project’s economic health, sustainability, and priorities. For those watching the crypto space closely, burn rate is one more factor to keep in mind when analyzing what makes a token valuable.